Projects have a starting point . Many project managers and scrum masters use a project charter to help kick start the flow of operation. A project charter is basically a document that outlines the mission and objectives for a company in its entirety. This documents helps to initiate the project. In essence, this is much like planning a race. It has a starting line and a finishing line. The project charter maps from start to finish. It serves as a foundational building block for many projects waiting to be embarked and operated on. Much like any other management plan, this will utilize tools and techniques such as expert judgement, business analytics, and meetings.
This is where Project schedule management comes into play. It is essentially a “structured timetable that project managers create to organize all project to-dos” (Andriiuk 2021). In other words, it is a detailed agenda that roadmaps the project deadlines and its milestones. Key components being a “schedule” of some sort. This is where many project teams will take its course of action. The project schedule management plan works in coordination with WBS or work breakdown structure. The WBS serves to “decompose the project into small achievable milestones” (Andriiuk 2021). Basically small check points are set in place to guide the work process little by little. Bit by bit. Chunk by chunk. That sort of thing.
In a general sense, this project schedule management plan consists of the following details:
- Project Schedule Model Development: This contains a schedule model that lists the logistics of the project. The logistics being the project activities and it’s estimated duration, any product dependencies, and its planning features.
- Level of Accuracy and Units of Measure: This focuses heavily on the specifics to details as well as consistency within planning for a project. The numbers and deadlines are considered to be the most important for measuring a products efficiency and accuracy. Deadlines are enforced to set milestones or check points for a deliverable or product to be completed on. This makes it so that the project teams are on agenda and up to date with their daily tasks. Time is measured in hours, days, or any other units. Numbers for the most part focuses on the amount of units the products are produced or rather the quantity that are being produced. Whether there is more or less of the quantity amount being manufactured to the consumer in a timely and cost efficient manner. Product operations are taken into account for the quantity being manufactured.
- Control Thresholds: The thresholds are measurable in variance which is the plus minus 10 percent. These variance thresholds monitor schedule performance. Like how in sports games, the coaches and sports analytics would use the plus minus to measure the player’s stats in a game. The little attention to detail for the statistics will help measure product performance for the project team.
- Rules of Performance Measurement: This process is done through percentages. It is a measurable progression track that covers how much work is being done for the project.
- Reporting formats: Projects more often than not have some sort of report or document to record its status and track records. It helps to provide information on where this project is at in terms of progression for the milestone or deadline. This ensures that project managers have a recollected record of the project and its details to show to the public in case of a business meeting. It is a form of written document that can be used to present to the world.
- Process Descriptions: Like the name suggests, this lists out all the details and descriptions in regards to how the the schedule management process will be executed for the project team. The specifics of what the project entails are examined into detail.
Defining Activities
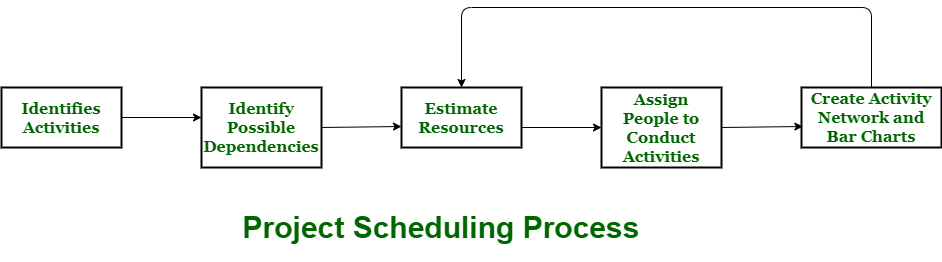
It is necessary to describe the details of activities listed in a project schedule management plan. Project teams often create a track record that includes the activity list, activity attributes, a milestone list, change requests from customers and stake holders, and updates to the project. This is to ensure that everything that is done in a project are being recorded for future use.
The activity list shows a list of activities that are involved within a project. That sounds pretty basic right? You sure bet it is! This activity list has the name of the activity, the identifier (ID) or number for the activity, and a brief description of what the activity is about.
Next is the activity attributes. The activity attributes basically extends the activity list into more specific details. It contains more information about schedule-related processes. Schedule-related processes such as the resource requirements, constraints, limitations, proposed dates, predecessors, successors, assumptions, etc. This goes into more depth about the activities.
Both the activity list and activity attributes should follow within the WBS agenda. Project teams would use automated systems to keep a track record of the activities being performed during a project phase. It makes it easier to collect information in a quick and efficient manner.
As mentioned before, milestones are very crucial for the duration of the entire project. Milestones are check point markers that identifies essential activities being performed at that time. Milestones are useful tools to monitor the project progress and helps with scheduling.
So why do we need to define activities in schedule managing? The answer is pretty simple. It is to make sure that the project team knows what the heck they are doing and understand how the work is being done for the project scope. This makes it easier for them to schedule and time manage in future project endeavors. And much later down the line when the project becomes more complex and tough to hurdle over.
Activities serve as elements of work being performed on a given task. Projects have duration, costs and finances, and resource requirements. It is imperative that the scrum masters in a project team review these activity lists and attributes with other members such as stakeholders before progressing.
The scrum masters are there to keep the stakeholders updated by presenting them the project reports and activities agenda. Then the stakeholders help by providing their inputs and sometimes would make change requests to be later implemented into the product. This ensures that scheduling is taken place to ensure that the project will be completed on time for its next milestone or deadline.
Sources:
Andriiuk, A. (2021, June 17). All about project scheduling. A Complete Guide. Retrieved February 19, 2022, from https://www.forecast.app/blog/project-scheduling
Schwalbe, K. (2019). Information Technology Project Management. Cengage Learning.

Leave a comment